The word “malware” generates bone-chilling mental images of computers and their operating systems suddenly crashing!
And with good reason.
Today, everyone relies on their computers and phones to manage their daily lives. As a result, these devices store a lot of sensitive information.
Computer viruses can cause severe damage to a business, including data loss or theft, hardware failure, or prolonged operating system outages.
A malware attack on a company can cost on average $2.4 million, and it cost the company 50 days that could have been spent being productive.
Malware attacks can lead to costly disruptions that your business might not be able to afford.
In an age where everyone is concerned about their privacy online and the safety of their operating systems, it’s more important now than ever to stay informed on how to stay protected.
What is Malware?
The term “malware” is a combination of the words “malicious” and “software.”
It has become an umbrella term for any software that is either intentionally or accidentally installed onto your machine to damage, steal or block your information.
There are different types of malware—some of the most infamous types of malware being trojans, ransomware, spyware, and viruses.
Cybercriminals use them to gain access to your sensitive information such as your financial details and your passwords.
How to protect yourself from malware?
Another easy way to avoid being attacked by a Trojan is to NEVER download software from a site you don’t know or trust.
This is the same for opening email attachments or installing a program sent to you by a stranger.
Luckily, most suspicious emails are sent straight to the spam folder but if one does manage to slip into your inbox, it’s best to just delete it without opening it.
You should also make sure your security software is up to date and that you have trusted antivirus software installed.
10 Most Common Types of Malware
But with not many knowing more about the common types of viruses that could attack our machines.
Trojans

Have you heard of the Trojan Horse? This was how ancient Greek soldiers could sneak into the city of Troy and destroy it!
This is what a trojan virus can do to your system if you’re unlucky enough to get one.
Trojan horses can look like anything.
Hackers can disguise this malware program to look like apps, free games, email attachments, and even anti-malware software.
For this reason, you should NEVER open an email from a danger, even if it’s from a bank.
For apps and free games, it might be a good idea to do some research online to see what others have to say about them.
Unlike other computer viruses, trojans rely on unsuspecting users to spread the virus.
Like the Greek soldiers in the Trojan War, trojan malware opens the symbolic gates of your system to all sorts of nefarious cybercriminals.
You’ll know that your system has fallen victim to a trojan when your machine starts to slow down and there’s a spike in internet usage. The most common sign of being infected by a Trojan includes suddenly freezing or crashing over and over again.
Spyware and Adware
Spyware likes to hide in an infected computer system, collecting as much information as possible on the unsuspecting user.
For this reason, attackers tend to use spyware to keep track of people they know and even people they don’t, celebrities for example.
Spyware works with other malware such as trojans or keyloggers to fool users into downloading it onto their machine.
Keyloggers
Keyloggers malware is a sneaky type of malware that monitors your typing and other activity on your machine to steal sensitive information.
The tricky part is that employers often use legal keylogger programs to keep tabs on their workers.
Keyloggers turn harmful when hackers and cybercriminals use them for nefarious means.
Attackers will often send an email with a link to a fake login page that will look like it’s from your bank.
In this way, hackers get you to type in your passwords and other sensitive data. Subsequently, they can see every single key that you type into this fake page.
Viruses
But not all malware is a virus.
A virus can infect computer files through a malicious code that has been embedded into another program.
Then all the malware has to do is wait. It will wait until the user accesses and processes the infected file. The virus will then duplicate itself and spread across the files and programs on the computer.
Worms

Worms can work independently of their host files and spread quickly throughout your network.
Like other malware, worms are used to steal confidential information and delete files.
But worms don’t need an infected program to infect your machine. Worms can take advantage of any weaknesses in your software.
Worms can even infect your machine with an instant message (IM). Without any anti-virus protection on your machine, your system will be vulnerable to a worm infection.
Hackers can also infect your IT network by sending a file with the worm attached to it in an email.
Worms that have spread throughout your machine will slow down your computer by taking up free hard drive space.
The virus will stealthily work through your files, changing them, and maybe even deleting them. Worms can even add EXTRA malware to your machine.
Another sign of worm infection in your machine is random files disappearing from your system.
Ransomware
Ransomware is one of the most damaging and harmful types of malware out there. This malware allows cybercriminals to hold your information for ransom.
Attackers use ransomware to encrypt and prevent users from accessing their information.
Once access has been blocked, hackers will often demand that users pay a ransom to retrieve their information.
Unfortunately, paying the hacker’s ransom rarely see access returned.
Polymorphic malware
To remain almost undetectable, polymorphic malware will adapt parts of itself with every file that it infects.
This can sometimes be a slow process to ensure that you can’t detect the full extent of the damage done to your machine by the malware.
Rootkits
It often leads to endpoint protection being blocked.
It can take control of your machine and work on your machine remotely. Not only that, but it can open hidden browsers and make money for its creator by clicking on ads.
One way to tell if your machine has been infected with rootkit malware is that your machine is repeatedly infected by other malware despite your antivirus software removing infected files.
Bots
They’ve been used to automate certain tasks and provide information. Without bots this would have been done by a human being.
The trouble comes when criminals use bots to carry out illegal activities.
They use the internet to connect your computer to many other computers outside your network.
Bots connect to your machine to a control center that can be made from one or multiple servers. This control center will also be connected to machines that have been infected just like yours.
This can help attackers bring a website down by flooding it with a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack.
Criminals will also be able to use bots to constantly click on adverts and generate revenue.
Bots can also collect email addresses and send spam emails.
Mobile Malware
Android devices, in particular, are targeted by attackers because there are more users compared to Apple.
Mobile malware operates similarly to any other malicious software that can infect a computer.
Unlike computer viruses, this malware program can be more dangerous for various reasons. This includes being able to infect your mobile phone through Bluetooth, especially with older Android systems.
Mobile Malware
Android devices, in particular, are targeted by attackers because there are more users compared to Apple.
Mobile malware operates similarly to any other malicious software that can infect a computer.
Unlike computer viruses, this malware program can be more dangerous for various reasons. This includes being able to infect your mobile phone through Bluetooth, especially with older Android systems.
Famous Malware Attacks
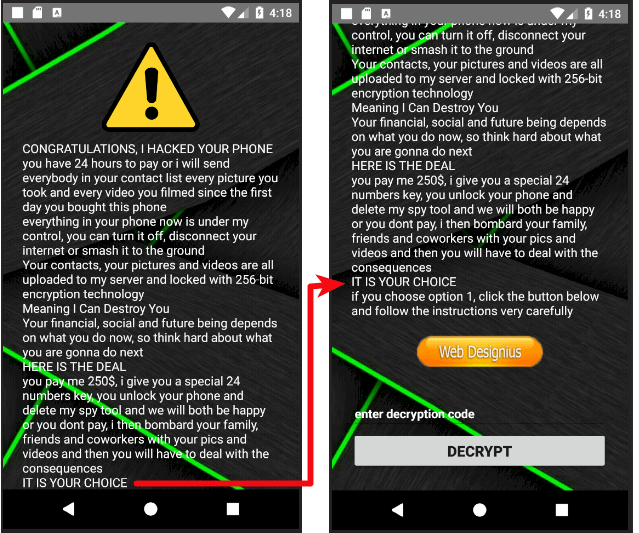
One of the most famous malware attacks took place as recently as 2020. The COVID-19 pandemic gave cybercriminals ample opportunities to exploit innocent users.
The CovidLock ransomware infected the victim’s computer by promising to offer more information about Covid-19 and sending infected files.
Once the files were installed, the ransomware managed to access and encrypt information found on Android gadgets and blocked users from accessing the data.
Users were then told that they needed to pay USD 100 per device to regain their information.
The victims were told to pay the pay ransom through Bitcoin and that if they refused to pay, the hackers would release all the private information to the public.
The Emotet Trojan became infamous for being one of the most harmful and destructive malware programs, in 2018, by the US Department of Homeland Security.
Criminals used this trojan to steal financial login information and cryptocurrencies. The malware spread through emails that were either phishing schemes or spam. One of the main examples was the case of the Chilean bank, Consorcio, which suffered damages of USD 2 million.
Hackers and cybercriminals have always been to find ways to exploit a potential victim’s weaknesses. They would even go so far as to exploit lonely people who are looking for Mr. or Mrs Right.
One of the first cases of social engineering used in a malware attack was the ILOVEYOU worm in 2000.
It was an email that tricked users into thinking it was a love letter. It managed to spread and infect more than 45 million people and cause over USD 15 billion in damages.
Malware examples
CCleaner is software that was created to remove unwanted files and unwanted software from a computer.
Sadly, it has been considered harmful because of all the malware that was hidden by hackers.It was first created to be only as a Microsoft Windows application before a macOS version was released in 2012.
It was first launched in 2004, but in 2017, two different Trojan Horses were found in the software.
These were Trojan.Floxif and Trojan. Nyetya, inserted into the free versions of CCleaner version 5.33.6162 and CCleaner Cloud version 1.07.3191.
The Trojan Horses were used to gain information from infected computers, such as IP addresses and other information. The data would then be sent to a third party in the US.
CCleaner’s parent company, Avast Piriform, immediately tried to remedy the problem, but they soon discovered that it was more severe than they initially believed.
It was believed that more than two million users’ computers were infected.
A second malware attack targeted large companies such as Intel, Cisco, Microsoft, and even Google. This second attack infected more than 40 computers.
In 2015, popular downloading software uTorrent (a BitTorrent client) caused an uproar when it was revealed that it had secretly installed cryptocurrency mining software.
According to an Extreme Tech report, users who installed uTorrent got unwanted software called Epic Scale.
The software would mine cryptocurrency while your machine was idle. Many user’s computers became damaged due to high usage.
A user’s computer system would slow down, and the CPU usage would run at a constant 80-100 percent.
According to a Verge report, BitTorrent had admitted to including Epic Scale but denied that it was done without the users’ consent.
In a statement to Verge, BitTorrent maintained that users had accepted the software before installing uTorrent and that it was strictly optional for users to download.
So, what does this all mean for businesses and you?
Today, the internet has become a necessity for doing business and communicating. The COVID-19 pandemic shone a spotlight on what a valuable tool the internet is to maintain business continuity even during the toughest of times.
This makes it vital now more than ever to stay informed about not only the benefits, but also the risks, of your hardware becoming yet another victim to a costly malware attack.
Schedule an appointment with Triadanet today and get the best advice available to make your business cyber-secure.
So, why wait? There is no time like the present.
Keep Your Small Business Safe!

